Table of Contents
Archiving Workflow
This workflow is optimized for a community-based, collaborative archiving project. The project leverages free and open source tools (especially Zotero and Eprints). See also USGS Workflow
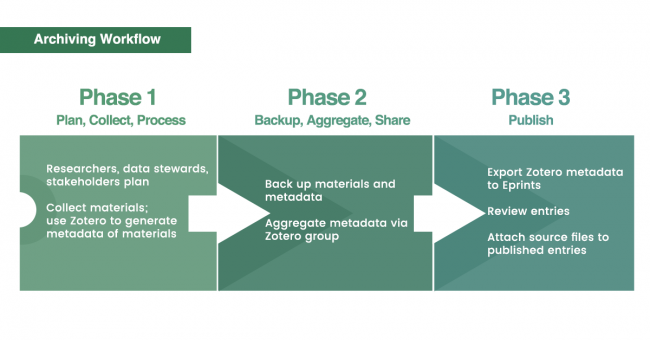
== Phase 1: Plan, Collect, Process ==
- researchers, data stewards, stakeholders plan the archival project
- an individual researcher starts an individual collection, acquires materials and reference them using the Zotero reference management system. Zotero is used primarily to generate and aggregate metadata.
- an individual researcher organizes her individual COLLECTION in one directory, with subdirectories as collection categories or subcategories, and with files named according to a filenaming convention according to a documented archival project plan.
- issues to taken in this phase include (among others): data management; filenaming convention; media formats, resolutions; preservation or sharing files. See also Digital Humanities Archiving.
Tip: When linking an entry's metadata to source file, use “Attach link to file” or “Attach link to URL” instead of “Attached stored copy of file.” See more tips.
== Phase 2: Back up, Aggregate, Share==
- researchers start backing up and sharing their individual collections with data stewards using Resilio Sync.
- researchers aggrege their collections via a closed or private Zotero group (required: free registration at zotero.org). Only the collection metadata are aggregated. Source files stay with individual researchers and are backed up by data stewards. The researcher shares his collection by dragging it to the appropriate directory in the group library.
- researchers, data stewards, stakeholders manage the quality of the aggregated collection according to the archival project plan.
== Phase 3: Publish==
- data stewards publish the aggregated collection online as a general catalog using the Eprints publicly searchable archive or repository. For heavy video and audio files, the Avalon Media System is the recommended publication platform. In this case, the metadata (with its link to Avalon) is still published concurrently in Eprints.
- researchers have to verify the accuracy of published online catalog.
Metadata from Phase 2 are exported to Eprints using BibTex, the only format common between Zotero and Eprints. In the publication, special characters, subtypes and other special metadata fields from Zotero or from the collection stage may not be mapped perfectly. Some data fields from Zotero may not even be included in the export. Adjustments have to be made on the publication platform itself. No Zotero metadata are lost, but published entries on Eprints may vary from Zotero records.
Copyleft or copyright concerns have to be addressed in Phase 3. Those source materials that can be shared publicly have to be uploaded and linked to appropriate repository entries.
Tip: For managers of Eprints publicly searchable archive or repository, note that metadata imported from Zotero are kept temporarily in the uploader's userspace. They have to be individually moved by the uploader to a common space where Reviewers can review and polish the entries. See also eprints-deposits.